- Aug 26, 2025
- ERP/CRM Applications
- 2353
Share this post on:
Managing multiple business operations at once can quickly become overwhelming. As a business owner, precision is crucial—yet manually handling various tasks often leads to operational inefficiencies, financial discrepancies, and customer management issues. Disconnected systems complicate data consolidation, making integration difficult. As your business grows, effectively handling large volumes of data from multiple departments becomes increasingly challenging.
So, what’s next? How do businesses handle all these challenges while maintaining business productivity and efficiency? What is the solution? The solution is ERP Integration. The ERP software market in Australia is booming and is expected to reach $1.08 billion by 2030. With that, ERP systems are becoming the top choice of enterprises in Australia, as they are looking to streamline their operations and enhance efficiency.
Key Takeaways:
ERP platforms unify key business functions, ensuring consistent data and automated workflows.
Integration requires planning, data migration, customization, and testing for smooth operations.
ERP integration enhances efficiency, accuracy, and visibility, while also supporting scalability and compliance.
ERP systems should be customized and scalable to support growth and long-term value.
Ongoing support, updates, and training are key to sustaining ERP performance and ROI.
How Does an ERP System Work?
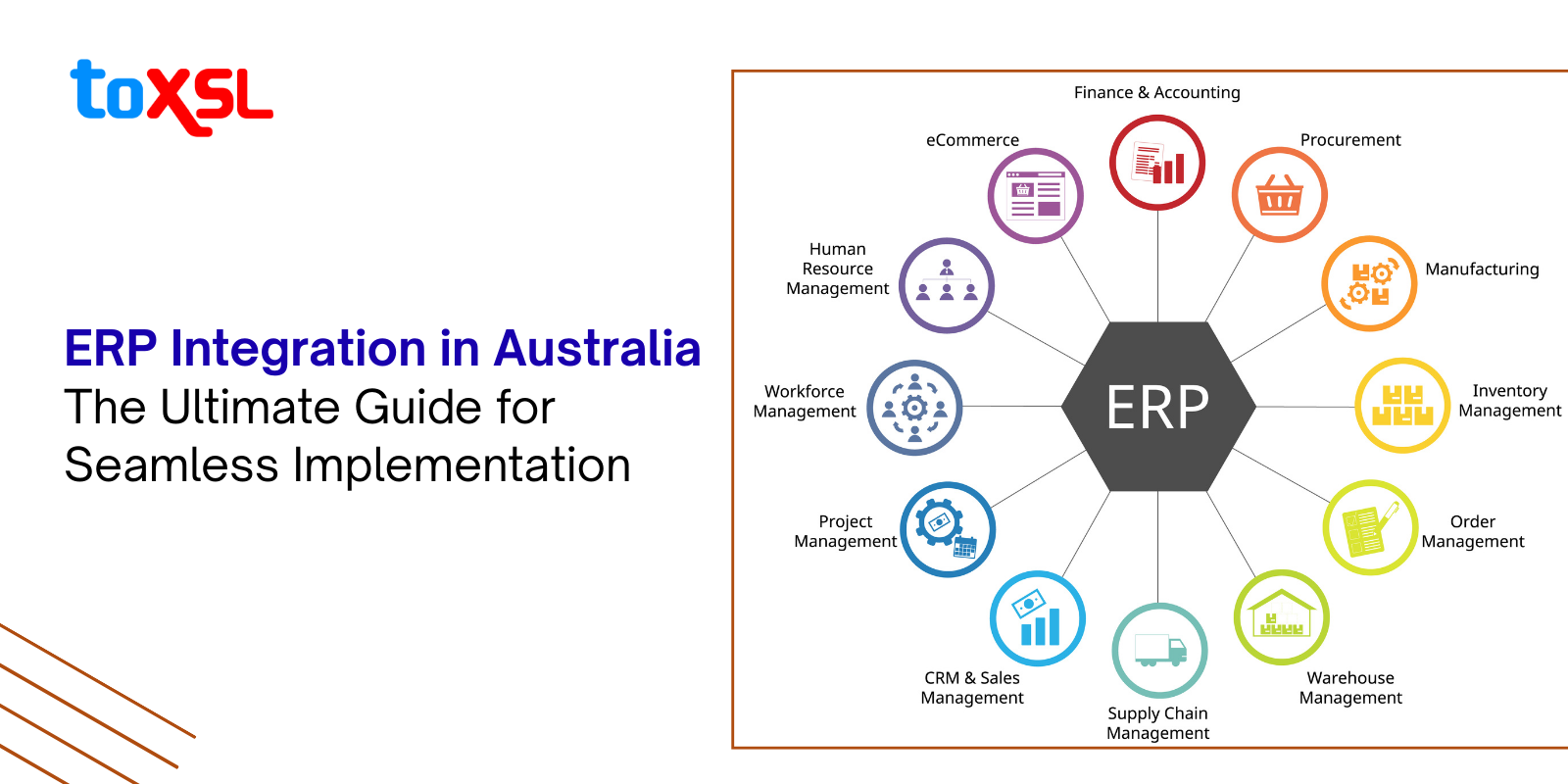
At its core, an ERP system functions as an interconnected software platform that centralizes data and automates workflows across the various departments within a business. It integrates various functions such as finance, sales, manufacturing, inventory, human resources, and more into a single, cohesive system. The primary principle behind ERP is the development of a “single source of truth”- all business data is stored in a shared database that is accessible to authorized individuals. For example, when the sales team inputs an order, the inventory levels automatically update, and production schedules may adjust accordingly. Modern ERP systems use application programming interfaces (APIs), middleware, and integration platforms to seamlessly communicate not only internally but also with external legacy systems and specialized third-party applications.
How to Integrate an ERP Software?
Assess and Plan: Start by defining the objectives for ERP integration—whether it’s streamlining operations, improving data accuracy, or enhancing customer experience. Conduct a thorough assessment of the existing IT infrastructure, including databases and systems, to understand what can be integrated and identify gaps. A detailed integration plan outlining scope, timeline, and goals will guide the process effectively.
Choose the Right ERP System and Integration Method: Selecting an ERP that aligns with your business needs, scalability requirements, and existing software ecosystems is crucial. Depending on your architecture and integration complexity, choose from available methods like:
API-based integration for streamlined communication
- Middleware (ESB) for robust data orchestration
- iPaaS for cloud-based, flexible integration
- Point-to-point integration for simpler, direct connections
- Cloud-based iPaaS options are increasingly popular due to their scalability, customization capabilities, and ease of use.
Customize and Configure: Customize the ERP system to fit the specific workflows and data requirements of your business. This step may involve creating custom fields, setting up automated workflows, and integrating third-party applications. Collaborate closely with ERP vendors or integrators who can provide expert support during this critical configuration phase.
Data Migration and Mapping: Migrate your existing data carefully, ensuring accuracy and consistency. This involves data cleansing, mapping fields between ERP and other applications, and validating data integrity. Proper mapping ensures that business functions like finance, inventory, and customer management work seamlessly with synchronized data.
Testing: Before going live, comprehensively test the integration scenarios to detect and resolve errors. Testing verifies data flows internal and external to the ERP, synchronizes operations across systems, and ensures reliable performance. This step helps reduce disruptions at launch.
Deployment and Monitoring: Enable the integration for live operation, followed by continuous monitoring to address any issues promptly. Set up automated synchronization schedules or real-time data flows as per business requirements. Many integration platforms also support ongoing maintenance and support services to optimize performance over time.
Read More: How to Integrate Inventory Tracking with Advanced Supply Chain Management
Benefits of Integrating an ERP Software
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are a cornerstone of modern business operations, serving as a centralized platform for managing vital processes such as finance, inventory, human resources, procurement, and customer relations. But the true power of ERP is unlocked through integration with existing business applications and systems. Integrating ERP software offers a host of benefits that streamline operations, improve data accuracy, and empower businesses to scale efficiently.
Improved Efficiency and Automation: One of the most immediate benefits of ERP integration is the automation of manual tasks and processes across departments. By connecting ERP with other business tools—such as CRM, e-commerce platforms, and accounting software—data flows automatically, eliminating the need for repetitive manual data entry. This reduces administrative overheads and frees employees to focus on more strategic tasks, increasing overall productivity and reducing human error.
Real-Time Data Visibility: ERP integration creates a unified data environment, providing real-time visibility into all facets of operations. Sales teams, inventory managers, and customer service representatives gain instant access to up-to-date information such as inventory levels, order statuses, and customer histories. This transparency helps teams make faster, more informed decisions and react swiftly to market changes or operational issues.
Enhanced Accuracy and Reduced Errors: Manual processes are prone to data duplication and errors, which can disrupt business workflows and lead to costly mistakes such as shipping errors or inaccurate billing. An integrated ERP system ensures data consistency by automatically synchronizing information across platforms, improving data quality, and minimizing the risk of costly errors. This creates a reliable foundation for analytics, forecasting, and compliance reporting.
Streamlined Order and Inventory Management: ERP integration turns your system into a single source of truth across sales channels and warehouses. Inventory levels are updated in real time, order processing is automated, and fulfillment errors are reduced. This seamless coordination optimizes stock management, helping maintain lean inventory levels, avoid stockouts, and improve customer fulfillment times. More efficient supply chain management also contributes to cost reductions.
Cost Savings: By reducing manual workloads, minimizing errors, and improving inventory management, ERP integration delivers significant cost savings. It prevents costly mistakes such as chargebacks, reduces IT overhead by consolidating systems, and eliminates the need to switch between incompatible platforms. Furthermore, better vendor and procurement management enhances negotiating power and efficiency.
Scalability and Flexibility: As companies grow, the complexity and volume of data increase. Integrated ERP systems provide the infrastructure to handle expanding operations without requiring a proportional increase in workforce or resources. Integration enables the ERP to adapt and connect with additional applications, supporting diverse business needs and future growth without the need for costly system overhauls.
Better Customer Experience: An integrated ERP system provides customer-facing teams with accurate, real-time data on orders, pricing, and inventory that ensures faster response times and more reliable service. Seamless channel synchronization means customers experience consistency in pricing and product availability, leading to improved satisfaction and loyalty. Additionally, better coordination across departments supports personalized service and quicker issue resolution.
Enhanced Collaboration and Mobility: ERP integration fosters greater collaboration not only within internal teams but also with external partners such as suppliers and customers. Sharing accurate and timely data helps streamline procurement, order fulfillment, and billing processes across the supply chain. Cloud-enabled ERP integration further empowers remote workers and mobile teams with access to critical business data anytime, anywhere.
Improved Compliance and Reporting: For businesses operating in regulated industries, integration ensures that critical compliance and financial data are automatically captured and consolidated for audits and regulatory reporting. Integrated systems can generate comprehensive reports with up-to-date, accurate information, reducing the risk of non-compliance and penalties. This facilitates better governance and more transparent business operations.
Cost of Integrating an ERP Software
Integrating an ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software system is a significant investment for any business, especially in Australia, where regulatory requirements and market dynamics shape integration strategies. Understanding the costs involved—and what drives those costs—is essential for proper budgeting and maximizing the return on investment.
Below is a comprehensive look at the typical costs associated with ERP integration in Australia in 2025, followed by a detailed discussion of the key cost factors businesses should consider.
Business Size | Estimated Cost Range (AUD) | Typical Timeline | What’s Included |
Small Businesses | 8,000 – 20,000 | 3 to 6 months | Software licenses, basic customization, data migration, initial training |
Mid-Market Businesses | 20,000 – 50,000+ | 6 to 9 months | More advanced customization, multiple integrations, extended training and support |
Large Enterprises | 50,000 – 150,000+ | 9 months to 1+ year | Extensive customization, large-scale data migration, complex system integration, comprehensive training, ongoing support |
Key Factors Influencing ERP Integration Costs
Business Size and Complexity: Larger organizations typically have more diverse operations and require extensive ERP capabilities. This leads to additional modules, deeper customization, and more complex data migration efforts, which increase the overall cost.
Level of Customization: Standard ERP packages provide numerous out-of-the-box functions, but most businesses require tailoring to fit unique workflows, reporting, compliance needs, and industry specifics. Customization can add 10-30% or more to the total budget, depending on complexity.
Data Migration and Quality: Migrating historical data from legacy systems to the ERP involves extraction, cleansing, validation, and import. Poor quality or large volumes of data increase the effort and thus the cost of migration significantly.
Type of Systems to Integrate: The more existing systems connected to the ERP (e.g., CRM, HRM, accounting, supply chain), the more complex the integration becomes. Each system adds additional interfaces and workflows to develop, test, and maintain.
Integration Technology: Choices such as using native ERP connectors, middleware platforms, bespoke APIs, or enterprise service buses influence the cost. Cloud-based integration platforms may reduce initial costs but have ongoing subscription fees.
Deployment Model: Cloud-based ERP systems often have lower upfront software costs with subscription pricing, but may have integration and data transfer fees. On-premise deployments carry higher hardware and licensing fees but may have lower ongoing costs depending on scale.
Employee Training: Successful ERP projects invest significantly in training and change management activities to ensure adoption. This includes creating training materials, conducting sessions, and supporting users during transition.
Ongoing Maintenance and Support: After implementation, ERP systems require regular updates, patches, and technical support. These recurring costs typically range from 15% to 20% of the initial software investment annually.
Conclusion:
ERP integration is a transformative undertaking that empowers Australian businesses to optimize operations, improve decision-making, and sustain competitive advantage. The process demands planning, the right technology, and expert guidance. ToXSL Technologies is a leading ERP development company, delivering customized solutions, technical excellence, and post-launch support designed specifically for the Australian market. With ToXSL, your ERP initiative becomes an engine for operational efficiency, compliance, customer satisfaction, and scalable growth. Contact us today and unlock the full potential of your business technology landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. What is ERP integration, and why is it important?
ERP integration connects your ERP system with other business applications to enable automated data sharing, reduce manual work, and provide a consolidated view of your operations, which improves accuracy and decision-making.
Q. How long does ERP integration typically take in Australia?
The duration varies but typically ranges from 3 to 6 months for small businesses, 6 to 9 months for mid-sized companies, and 9 months to over a year for large enterprises with complex needs.
Q. Can ERP integration be customized for specific business needs?
Absolutely. ERP integration is highly customizable to fit unique workflows, industries, and operational goals, ensuring the solution supports business strategies effectively.
Q. What factors influence the cost of ERP integration?
Major factors include business size, integration complexity, customization levels, data migration efforts, and the choice of integration technology.
Q. Why should businesses partner with ToXSL Technologies for ERP integration?
ToXSL offers deep ERP expertise, personalized solutions, modern technologies, a strong understanding of Australian market and compliance requirements, and committed ongoing support to ensure project success and business growth.











